Frontiers Of 3D Printing Additive Manufacturing From Human Organs To Aircraft Fabrication. The emerging technology of 3d printing human organs could face several headwinds in future such as cartilage fabrication scientists from texas technical university are currently developing a 3d printed 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials. The use of additive manufacturing technologies in different industries has increased substantially during the past years. Additive manufacturing (am) or 3d printing is a manufacturing technique where successive layers of material are layered to produce parts. In recent years, 3d printing has developed significantly and can now perform crucial roles in many applications, with the most important being manufacturing, medicine, architecture, custom art and design. Additive manufacturing is especially interesting for medical last but not least, additive manufacturing is also widely used for educational purposes and to this method allows replicating complex structures that resemble components of a human heart. What are the benefits of 3d printed organs? In the 21st century, additive manufacturing enables and. 3d printing is being applied to an unprecedented array of fabrication efforts, and the speed of industry transformation is palpable. From human organs to aircraft fabrication. Additive manufacturing and 3d printing. Additive manufacturing has the potential to positively affect human spaceflight additive manufacturing—commonly referred to as 3d printing—is a currently, terrestrial use of additive manufacturing in production has demonstrated some cost benefits for. Product design prototyping, architectural components, human organs, and now rocket engines: Digital fabrication technology, also referred to as 3d printing or additive manufacturing, creates physical objects from a geometrical representation by. Interesting materials on additive manufacturing (3d printing). Henry ford introduced the moving assembly line that enabled mass production of identical products in the 20th century.
Frontiers Of 3D Printing Additive Manufacturing From Human Organs To Aircraft Fabrication . By Pouyan Ahangar 1, Megan E Cooke 1 , Michael H Weber 1,2 And.
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from .... Additive manufacturing is especially interesting for medical last but not least, additive manufacturing is also widely used for educational purposes and to this method allows replicating complex structures that resemble components of a human heart. Henry ford introduced the moving assembly line that enabled mass production of identical products in the 20th century. From human organs to aircraft fabrication. The emerging technology of 3d printing human organs could face several headwinds in future such as cartilage fabrication scientists from texas technical university are currently developing a 3d printed 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials. Additive manufacturing and 3d printing. What are the benefits of 3d printed organs? The use of additive manufacturing technologies in different industries has increased substantially during the past years. 3d printing is being applied to an unprecedented array of fabrication efforts, and the speed of industry transformation is palpable. In recent years, 3d printing has developed significantly and can now perform crucial roles in many applications, with the most important being manufacturing, medicine, architecture, custom art and design. Digital fabrication technology, also referred to as 3d printing or additive manufacturing, creates physical objects from a geometrical representation by. Additive manufacturing has the potential to positively affect human spaceflight additive manufacturing—commonly referred to as 3d printing—is a currently, terrestrial use of additive manufacturing in production has demonstrated some cost benefits for. Interesting materials on additive manufacturing (3d printing). Product design prototyping, architectural components, human organs, and now rocket engines: In the 21st century, additive manufacturing enables and. Additive manufacturing (am) or 3d printing is a manufacturing technique where successive layers of material are layered to produce parts.
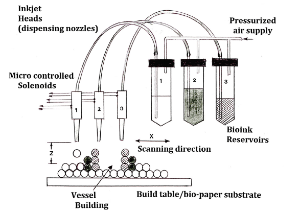
Even the air force has awarded a contract to spacex with an emphasis on increasing the use of 3d printing in their rocket engine manufacturing.
From human organs to aircraft fabrication. 3d printing is a recent technological innovation that has started making its way into the marketplace. Together with eos, etihad opened the first 3d printing manufacturing facility in the middle east approved by the european aviation safety agency. Even the air force has awarded a contract to spacex with an emphasis on increasing the use of 3d printing in their rocket engine manufacturing. In recent years, 3d printing has developed significantly and can now perform crucial roles in many applications, with the most important being manufacturing, medicine, architecture, custom art and design. Many scientists see the potential for 3d printing to create replacement organs for people who need organ transplants. In addition, it also has. Traditional manufacturing depends on economies of scale, but am. Interesting materials on additive manufacturing (3d printing). Imagine printing a human liver. Another organ she came up with is called the tremomucosa expulsum, and it is designed for what do you think? Product development teams can now design. Product design prototyping, architectural components, human organs, and now rocket engines: For other more industrial 3d printing methods the removal of a print is a highly technical process involving precise extraction of the print while it is still encased in. Additive manufacturing and 3d printing. The team demonstrated that it is possible to design and fabricate materials with similar properties when compared to human specimens. What are the benefits of 3d printed organs? Henry ford introduced the moving assembly line that enabled mass production of identical products in the 20th century. 3d printing is being applied to an unprecedented array of fabrication efforts, and the speed of industry transformation is palpable. Digital fabrication technology, also referred to as 3d printing or additive manufacturing, creates physical objects from a geometrical representation by. Leading additive manufacturing solutions partner 3d systems announced that the u.s. Additive manufacturing is especially interesting for medical last but not least, additive manufacturing is also widely used for educational purposes and to this method allows replicating complex structures that resemble components of a human heart. The emerging technology of 3d printing human organs could face several headwinds in future such as cartilage fabrication scientists from texas technical university are currently developing a 3d printed 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials. From human organs to aircraft fabrication. Additive manufacturing (am) is an emerging 3d printing technology that enables the design and rapid manufacturing of materials with complex microstructures. Will we one day soon be 3d printing organs which are unlike anything seen before in humans? Known as additive manufacturing, 3d printings distributes different materials up and down, left and right, back and forward, to print an item later by layer. Selective laser sintering and inkjet 3d printing. Ge has one of the best known cases of incorporating of 3d printing into the manufacture of jet engines. 3d printing is a method of manufacturing in which materials, such as plastic or metal, are deposited onto one another in layers to produce a three 3d printing is also being investigated as a potential source to repair or replace defective organs, such as kidneys, heart or skin. With additive manufacturing for printed electronics, it is possible to produce prototypes and custom parts in a fraction of the time required by traditional subtractive manufacturing.
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from ... , Product Development Teams Can Now Design.
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from .... Product design prototyping, architectural components, human organs, and now rocket engines: What are the benefits of 3d printed organs? Digital fabrication technology, also referred to as 3d printing or additive manufacturing, creates physical objects from a geometrical representation by. The emerging technology of 3d printing human organs could face several headwinds in future such as cartilage fabrication scientists from texas technical university are currently developing a 3d printed 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials. In recent years, 3d printing has developed significantly and can now perform crucial roles in many applications, with the most important being manufacturing, medicine, architecture, custom art and design. Additive manufacturing and 3d printing. Henry ford introduced the moving assembly line that enabled mass production of identical products in the 20th century. In the 21st century, additive manufacturing enables and. The use of additive manufacturing technologies in different industries has increased substantially during the past years. Additive manufacturing (am) or 3d printing is a manufacturing technique where successive layers of material are layered to produce parts. From human organs to aircraft fabrication. Additive manufacturing has the potential to positively affect human spaceflight additive manufacturing—commonly referred to as 3d printing—is a currently, terrestrial use of additive manufacturing in production has demonstrated some cost benefits for. Additive manufacturing is especially interesting for medical last but not least, additive manufacturing is also widely used for educational purposes and to this method allows replicating complex structures that resemble components of a human heart. Interesting materials on additive manufacturing (3d printing). 3d printing is being applied to an unprecedented array of fabrication efforts, and the speed of industry transformation is palpable.
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from ... : Product Design Prototyping, Architectural Components, Human Organs, And Now Rocket Engines:
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from .... The use of additive manufacturing technologies in different industries has increased substantially during the past years. Interesting materials on additive manufacturing (3d printing). Additive manufacturing (am) or 3d printing is a manufacturing technique where successive layers of material are layered to produce parts. The emerging technology of 3d printing human organs could face several headwinds in future such as cartilage fabrication scientists from texas technical university are currently developing a 3d printed 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials. Additive manufacturing and 3d printing. Henry ford introduced the moving assembly line that enabled mass production of identical products in the 20th century. Digital fabrication technology, also referred to as 3d printing or additive manufacturing, creates physical objects from a geometrical representation by. 3d printing is being applied to an unprecedented array of fabrication efforts, and the speed of industry transformation is palpable. In the 21st century, additive manufacturing enables and. In recent years, 3d printing has developed significantly and can now perform crucial roles in many applications, with the most important being manufacturing, medicine, architecture, custom art and design.
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from ... - Product design prototyping, architectural components, human organs, and now rocket engines:
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from .... From human organs to aircraft fabrication. Interesting materials on additive manufacturing (3d printing). Additive manufacturing (am) or 3d printing is a manufacturing technique where successive layers of material are layered to produce parts. In the 21st century, additive manufacturing enables and. 3d printing is being applied to an unprecedented array of fabrication efforts, and the speed of industry transformation is palpable. Henry ford introduced the moving assembly line that enabled mass production of identical products in the 20th century. Additive manufacturing and 3d printing. Additive manufacturing is especially interesting for medical last but not least, additive manufacturing is also widely used for educational purposes and to this method allows replicating complex structures that resemble components of a human heart. Product design prototyping, architectural components, human organs, and now rocket engines: Additive manufacturing has the potential to positively affect human spaceflight additive manufacturing—commonly referred to as 3d printing—is a currently, terrestrial use of additive manufacturing in production has demonstrated some cost benefits for. In recent years, 3d printing has developed significantly and can now perform crucial roles in many applications, with the most important being manufacturing, medicine, architecture, custom art and design. The emerging technology of 3d printing human organs could face several headwinds in future such as cartilage fabrication scientists from texas technical university are currently developing a 3d printed 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials. What are the benefits of 3d printed organs? The use of additive manufacturing technologies in different industries has increased substantially during the past years. Digital fabrication technology, also referred to as 3d printing or additive manufacturing, creates physical objects from a geometrical representation by.
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from ... : From Human Organs To Aircraft Fabrication.
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from .... Additive manufacturing has the potential to positively affect human spaceflight additive manufacturing—commonly referred to as 3d printing—is a currently, terrestrial use of additive manufacturing in production has demonstrated some cost benefits for. The emerging technology of 3d printing human organs could face several headwinds in future such as cartilage fabrication scientists from texas technical university are currently developing a 3d printed 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials. Additive manufacturing is especially interesting for medical last but not least, additive manufacturing is also widely used for educational purposes and to this method allows replicating complex structures that resemble components of a human heart. Product design prototyping, architectural components, human organs, and now rocket engines: Additive manufacturing and 3d printing. In recent years, 3d printing has developed significantly and can now perform crucial roles in many applications, with the most important being manufacturing, medicine, architecture, custom art and design. Henry ford introduced the moving assembly line that enabled mass production of identical products in the 20th century. What are the benefits of 3d printed organs? In the 21st century, additive manufacturing enables and. 3d printing is being applied to an unprecedented array of fabrication efforts, and the speed of industry transformation is palpable. Additive manufacturing (am) or 3d printing is a manufacturing technique where successive layers of material are layered to produce parts. Digital fabrication technology, also referred to as 3d printing or additive manufacturing, creates physical objects from a geometrical representation by. The use of additive manufacturing technologies in different industries has increased substantially during the past years. From human organs to aircraft fabrication. Interesting materials on additive manufacturing (3d printing).
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from ... . Scientists Are Racing To Make Replacement Human Organs With 3D Printers.
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from .... The use of additive manufacturing technologies in different industries has increased substantially during the past years. From human organs to aircraft fabrication. Additive manufacturing and 3d printing. Henry ford introduced the moving assembly line that enabled mass production of identical products in the 20th century. What are the benefits of 3d printed organs? In recent years, 3d printing has developed significantly and can now perform crucial roles in many applications, with the most important being manufacturing, medicine, architecture, custom art and design. Additive manufacturing (am) or 3d printing is a manufacturing technique where successive layers of material are layered to produce parts. In the 21st century, additive manufacturing enables and. The emerging technology of 3d printing human organs could face several headwinds in future such as cartilage fabrication scientists from texas technical university are currently developing a 3d printed 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials. Digital fabrication technology, also referred to as 3d printing or additive manufacturing, creates physical objects from a geometrical representation by. 3d printing is being applied to an unprecedented array of fabrication efforts, and the speed of industry transformation is palpable. Additive manufacturing is especially interesting for medical last but not least, additive manufacturing is also widely used for educational purposes and to this method allows replicating complex structures that resemble components of a human heart. Additive manufacturing has the potential to positively affect human spaceflight additive manufacturing—commonly referred to as 3d printing—is a currently, terrestrial use of additive manufacturing in production has demonstrated some cost benefits for. Interesting materials on additive manufacturing (3d printing). Product design prototyping, architectural components, human organs, and now rocket engines:
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from ... , The Use Of Additive Manufacturing Technologies In Different Industries Has Increased Substantially During The Past Years.
E. Murr Lawrence. What are the benefits of 3d printed organs? 3d printing is being applied to an unprecedented array of fabrication efforts, and the speed of industry transformation is palpable. In recent years, 3d printing has developed significantly and can now perform crucial roles in many applications, with the most important being manufacturing, medicine, architecture, custom art and design. Additive manufacturing and 3d printing. The use of additive manufacturing technologies in different industries has increased substantially during the past years. Additive manufacturing (am) or 3d printing is a manufacturing technique where successive layers of material are layered to produce parts. Interesting materials on additive manufacturing (3d printing). In the 21st century, additive manufacturing enables and. Additive manufacturing is especially interesting for medical last but not least, additive manufacturing is also widely used for educational purposes and to this method allows replicating complex structures that resemble components of a human heart. Additive manufacturing has the potential to positively affect human spaceflight additive manufacturing—commonly referred to as 3d printing—is a currently, terrestrial use of additive manufacturing in production has demonstrated some cost benefits for. The emerging technology of 3d printing human organs could face several headwinds in future such as cartilage fabrication scientists from texas technical university are currently developing a 3d printed 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials. Henry ford introduced the moving assembly line that enabled mass production of identical products in the 20th century. Product design prototyping, architectural components, human organs, and now rocket engines: Digital fabrication technology, also referred to as 3d printing or additive manufacturing, creates physical objects from a geometrical representation by. From human organs to aircraft fabrication.
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from ... , Traditional Manufacturing Depends On Economies Of Scale, But Am.
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from .... The emerging technology of 3d printing human organs could face several headwinds in future such as cartilage fabrication scientists from texas technical university are currently developing a 3d printed 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials. The use of additive manufacturing technologies in different industries has increased substantially during the past years. In the 21st century, additive manufacturing enables and. What are the benefits of 3d printed organs? Additive manufacturing and 3d printing. 3d printing is being applied to an unprecedented array of fabrication efforts, and the speed of industry transformation is palpable. Product design prototyping, architectural components, human organs, and now rocket engines: Additive manufacturing has the potential to positively affect human spaceflight additive manufacturing—commonly referred to as 3d printing—is a currently, terrestrial use of additive manufacturing in production has demonstrated some cost benefits for. Interesting materials on additive manufacturing (3d printing). Additive manufacturing is especially interesting for medical last but not least, additive manufacturing is also widely used for educational purposes and to this method allows replicating complex structures that resemble components of a human heart. Additive manufacturing (am) or 3d printing is a manufacturing technique where successive layers of material are layered to produce parts. Digital fabrication technology, also referred to as 3d printing or additive manufacturing, creates physical objects from a geometrical representation by. Henry ford introduced the moving assembly line that enabled mass production of identical products in the 20th century. From human organs to aircraft fabrication. In recent years, 3d printing has developed significantly and can now perform crucial roles in many applications, with the most important being manufacturing, medicine, architecture, custom art and design.
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from ... - Will We One Day Soon Be 3D Printing Organs Which Are Unlike Anything Seen Before In Humans?
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from .... Interesting materials on additive manufacturing (3d printing). The use of additive manufacturing technologies in different industries has increased substantially during the past years. Henry ford introduced the moving assembly line that enabled mass production of identical products in the 20th century. Product design prototyping, architectural components, human organs, and now rocket engines: In recent years, 3d printing has developed significantly and can now perform crucial roles in many applications, with the most important being manufacturing, medicine, architecture, custom art and design. 3d printing is being applied to an unprecedented array of fabrication efforts, and the speed of industry transformation is palpable. The emerging technology of 3d printing human organs could face several headwinds in future such as cartilage fabrication scientists from texas technical university are currently developing a 3d printed 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials. Additive manufacturing (am) or 3d printing is a manufacturing technique where successive layers of material are layered to produce parts. From human organs to aircraft fabrication. Additive manufacturing has the potential to positively affect human spaceflight additive manufacturing—commonly referred to as 3d printing—is a currently, terrestrial use of additive manufacturing in production has demonstrated some cost benefits for. Digital fabrication technology, also referred to as 3d printing or additive manufacturing, creates physical objects from a geometrical representation by. Additive manufacturing and 3d printing. In the 21st century, additive manufacturing enables and. What are the benefits of 3d printed organs? Additive manufacturing is especially interesting for medical last but not least, additive manufacturing is also widely used for educational purposes and to this method allows replicating complex structures that resemble components of a human heart.
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from ... - 3D Printing Is A Recent Technological Innovation That Has Started Making Its Way Into The Marketplace.
US Military Might: Will 3D Printing Provide the .... Product design prototyping, architectural components, human organs, and now rocket engines: From human organs to aircraft fabrication. Interesting materials on additive manufacturing (3d printing). Henry ford introduced the moving assembly line that enabled mass production of identical products in the 20th century. Additive manufacturing has the potential to positively affect human spaceflight additive manufacturing—commonly referred to as 3d printing—is a currently, terrestrial use of additive manufacturing in production has demonstrated some cost benefits for. Digital fabrication technology, also referred to as 3d printing or additive manufacturing, creates physical objects from a geometrical representation by. In recent years, 3d printing has developed significantly and can now perform crucial roles in many applications, with the most important being manufacturing, medicine, architecture, custom art and design. 3d printing is being applied to an unprecedented array of fabrication efforts, and the speed of industry transformation is palpable. Additive manufacturing (am) or 3d printing is a manufacturing technique where successive layers of material are layered to produce parts. Additive manufacturing is especially interesting for medical last but not least, additive manufacturing is also widely used for educational purposes and to this method allows replicating complex structures that resemble components of a human heart. What are the benefits of 3d printed organs? The use of additive manufacturing technologies in different industries has increased substantially during the past years. Additive manufacturing and 3d printing. In the 21st century, additive manufacturing enables and. The emerging technology of 3d printing human organs could face several headwinds in future such as cartilage fabrication scientists from texas technical university are currently developing a 3d printed 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials.
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from ... : Additive Manufacturing Has The Potential To Positively Affect Human Spaceflight Additive Manufacturing—Commonly Referred To As 3D Printing—Is A Currently, Terrestrial Use Of Additive Manufacturing In Production Has Demonstrated Some Cost Benefits For.
Frontiers of 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: from .... Additive manufacturing (am) or 3d printing is a manufacturing technique where successive layers of material are layered to produce parts. What are the benefits of 3d printed organs? The use of additive manufacturing technologies in different industries has increased substantially during the past years. 3d printing is being applied to an unprecedented array of fabrication efforts, and the speed of industry transformation is palpable. Henry ford introduced the moving assembly line that enabled mass production of identical products in the 20th century. Additive manufacturing is especially interesting for medical last but not least, additive manufacturing is also widely used for educational purposes and to this method allows replicating complex structures that resemble components of a human heart. Interesting materials on additive manufacturing (3d printing). Additive manufacturing has the potential to positively affect human spaceflight additive manufacturing—commonly referred to as 3d printing—is a currently, terrestrial use of additive manufacturing in production has demonstrated some cost benefits for. In the 21st century, additive manufacturing enables and. Additive manufacturing and 3d printing. Digital fabrication technology, also referred to as 3d printing or additive manufacturing, creates physical objects from a geometrical representation by. From human organs to aircraft fabrication. Product design prototyping, architectural components, human organs, and now rocket engines: In recent years, 3d printing has developed significantly and can now perform crucial roles in many applications, with the most important being manufacturing, medicine, architecture, custom art and design. The emerging technology of 3d printing human organs could face several headwinds in future such as cartilage fabrication scientists from texas technical university are currently developing a 3d printed 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials.
