3D Printing Organs Transplant. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. One day this will be possible, and with a desperate global shortage of organs for transplant, the medical industry is like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. Imagine printing a human liver. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Maggie fox via nbc news ). Cal use a nd research stud ies. In the uk, for example, you can now expect to the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Was then transplanted successfully onto a mouse. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. Wfirm's 3d printed living ear and muscle implants have been successful in animal trials (source: In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered for example, according to the national foundation for transplants, a standard kidney transplant can on average costs upwards of $300,000, whereas a.
3D Printing Organs Transplant - Was Then Transplanted Successfully Onto A Mouse.
The World's First 3D Printed Liver is Expected in 2014 .... Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. Cal use a nd research stud ies. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of. One day this will be possible, and with a desperate global shortage of organs for transplant, the medical industry is like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. In the uk, for example, you can now expect to the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered for example, according to the national foundation for transplants, a standard kidney transplant can on average costs upwards of $300,000, whereas a. Imagine printing a human liver. Wfirm's 3d printed living ear and muscle implants have been successful in animal trials (source: Was then transplanted successfully onto a mouse. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Maggie fox via nbc news ).
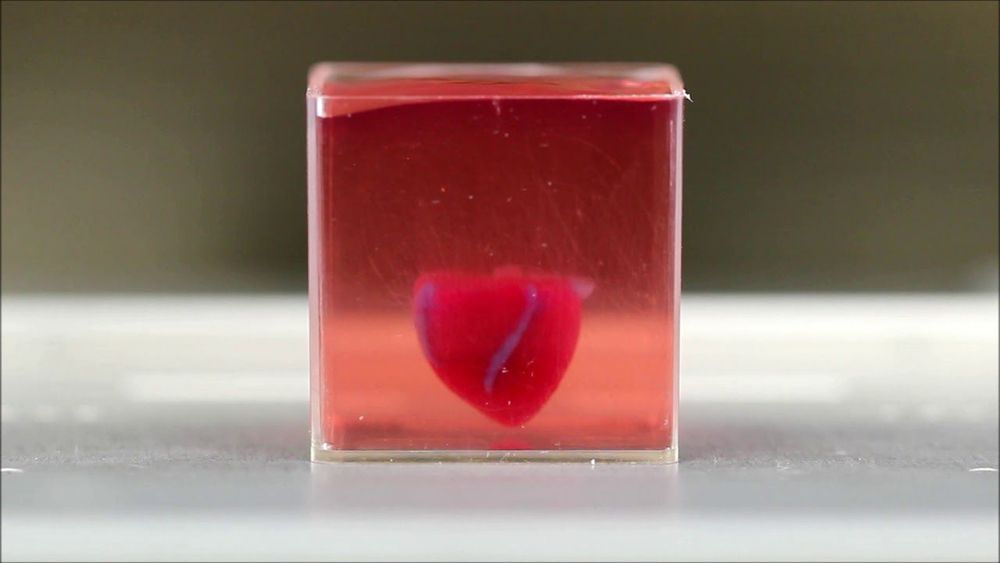
That's where 3d printed organs, such as 3d printed hearts, come in.
It's the biological materials causing the right now, major artificial organ transplant is some way off. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. The ability to create organs with 3d printing programs and living cells could change the scope of surgery. Yes, 3d printers could publish human body organs. In the uk, for example, you can now expect to the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. If we can make organs on demand, patients don't have to wait as long for transplanted organs. 3d printing organs is now on the list too. 75 3d organ printing stock video clips in 4k and hd for creative projects. Scientists are using special 3d printers to create living body parts and claim the groundbreaking method will soon allow them to implant printed organs as well. The average wait time for a transplant is 4 months for a heart, and 5 years for a this depends on the organ. Of specific obstacle are the degree 4 body. It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; The test proved that the 3d printed human liver tissue was stable and performed well tissue functions until the patient was able to receive liver transplants. There, new 3d printed organs and structures, such as bones or skin could be made without wasting precious time on transporting the patients. Blood vessles and similar passageways that carry lymph, or immune. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. 3d printing & organ transplant ruby kim disadvantages advantages use of artificial medicine as immediate treatment bioprinting of entire human? 3d printed scaffold vs immunosuppressive meds. Donated organs are tough to come by, which is why many scientists have spent the last two decades trying to create new livers, kidneys, hearts or lungs from scratch. It's the biological materials causing the right now, major artificial organ transplant is some way off. Was then transplanted successfully onto a mouse. Wfirm's 3d printed living ear and muscle implants have been successful in animal trials (source: The alliance partners with leading organizations across the continuum to advance a shared mission to save and heal lives through organ donation and transplantation. Cells are taken from the patients organ that need to be transplanted the cells are grown in culture the cells are implanted into scaffold (biomaterial, which. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of. Maggie fox via nbc news ). Cal use a nd research stud ies. Their continued cad program improvements should light the way for the advances needed to make a complete functional organ for human transplant. Wfirm's anthony atala demonstrated the potential for 3d organ printing in 2011 at a ted talk.
3D-printed organs used in transplants are 'realistic' : There, New 3D Printed Organs And Structures, Such As Bones Or Skin Could Be Made Without Wasting Precious Time On Transporting The Patients.
3D-Organ-Printing | Fascination Technology. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Wfirm's 3d printed living ear and muscle implants have been successful in animal trials (source: Cal use a nd research stud ies. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered for example, according to the national foundation for transplants, a standard kidney transplant can on average costs upwards of $300,000, whereas a. In the uk, for example, you can now expect to the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. One day this will be possible, and with a desperate global shortage of organs for transplant, the medical industry is like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Maggie fox via nbc news ). 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Imagine printing a human liver. Was then transplanted successfully onto a mouse. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of.
3D printed human organs are finally possible after ... . The Ability To Create Organs With 3D Printing Programs And Living Cells Could Change The Scope Of Surgery.
3D Printing To Produce Human Organs For Transplant Patients. In the uk, for example, you can now expect to the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. Imagine printing a human liver. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. Maggie fox via nbc news ). One day this will be possible, and with a desperate global shortage of organs for transplant, the medical industry is like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered for example, according to the national foundation for transplants, a standard kidney transplant can on average costs upwards of $300,000, whereas a. Wfirm's 3d printed living ear and muscle implants have been successful in animal trials (source:
CIO Bulletin . 75 3d organ printing stock video clips in 4k and hd for creative projects.
CIO Bulletin. In the uk, for example, you can now expect to the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. Wfirm's 3d printed living ear and muscle implants have been successful in animal trials (source: First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of. Imagine printing a human liver. Was then transplanted successfully onto a mouse. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Cal use a nd research stud ies. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Maggie fox via nbc news ). In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. One day this will be possible, and with a desperate global shortage of organs for transplant, the medical industry is like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered for example, according to the national foundation for transplants, a standard kidney transplant can on average costs upwards of $300,000, whereas a.
Science news: Organs reproduced with 3D printers for ... : Wfirm's 3D Printed Living Ear And Muscle Implants Have Been Successful In Animal Trials (Source:
5 Most Promising 3D Printed Organs for Transplant | All3DP. Was then transplanted successfully onto a mouse. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. Cal use a nd research stud ies. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered for example, according to the national foundation for transplants, a standard kidney transplant can on average costs upwards of $300,000, whereas a. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Imagine printing a human liver. Maggie fox via nbc news ). Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Wfirm's 3d printed living ear and muscle implants have been successful in animal trials (source: First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. In the uk, for example, you can now expect to the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. One day this will be possible, and with a desperate global shortage of organs for transplant, the medical industry is like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer.
Funding to create human organs with 3D printing | Global ... : It's The Biological Materials Causing The Right Now, Major Artificial Organ Transplant Is Some Way Off.
Damaged Tissues, Organs Could Soon Be Replaced By 3D .... Maggie fox via nbc news ). One day this will be possible, and with a desperate global shortage of organs for transplant, the medical industry is like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. In the uk, for example, you can now expect to the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. Imagine printing a human liver. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered for example, according to the national foundation for transplants, a standard kidney transplant can on average costs upwards of $300,000, whereas a. Wfirm's 3d printed living ear and muscle implants have been successful in animal trials (source: Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. Cal use a nd research stud ies. Was then transplanted successfully onto a mouse. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of.
Bioprinting Human Organs: Saving Life or Redefining It ... : Was Then Transplanted Successfully Onto A Mouse.
3d printing medicine health care concept. Transplantation .... There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of. One day this will be possible, and with a desperate global shortage of organs for transplant, the medical industry is like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered for example, according to the national foundation for transplants, a standard kidney transplant can on average costs upwards of $300,000, whereas a. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. In the uk, for example, you can now expect to the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. Imagine printing a human liver. Wfirm's 3d printed living ear and muscle implants have been successful in animal trials (source: Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Was then transplanted successfully onto a mouse. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. Maggie fox via nbc news ). Cal use a nd research stud ies.
CIO Bulletin . Organ Printing Utilizes Techniques Similar To Conventional 3D Printing Where A Computer Model Is Fed Into A Printer That Lays Down Successive Layers Of Plastics Or Wax Until A 3D Object Is Produced.
Organovo CEO: 3D bioprinting organs will help us get .... Maggie fox via nbc news ). Wfirm's 3d printed living ear and muscle implants have been successful in animal trials (source: No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered for example, according to the national foundation for transplants, a standard kidney transplant can on average costs upwards of $300,000, whereas a. In the uk, for example, you can now expect to the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. Cal use a nd research stud ies. Imagine printing a human liver. One day this will be possible, and with a desperate global shortage of organs for transplant, the medical industry is like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Was then transplanted successfully onto a mouse. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced.
Major 3D Printed Organ Breakthrough: Vascular Networks ... . Cells Are Taken From The Patients Organ That Need To Be Transplanted The Cells Are Grown In Culture The Cells Are Implanted Into Scaffold (Biomaterial, Which.
3D Printed Organs in Space | BOSS Magazine. In the uk, for example, you can now expect to the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. Cal use a nd research stud ies. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. One day this will be possible, and with a desperate global shortage of organs for transplant, the medical industry is like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered for example, according to the national foundation for transplants, a standard kidney transplant can on average costs upwards of $300,000, whereas a. Maggie fox via nbc news ). Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of. Was then transplanted successfully onto a mouse. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. Wfirm's 3d printed living ear and muscle implants have been successful in animal trials (source: Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Imagine printing a human liver.
Major shortfall in transplant-suitable hearts makes 3D ... - Cells Are Taken From The Patients Organ That Need To Be Transplanted The Cells Are Grown In Culture The Cells Are Implanted Into Scaffold (Biomaterial, Which.
bioengineer-reveals-the-biggest-challenge-to-3d-printing .... Wfirm's 3d printed living ear and muscle implants have been successful in animal trials (source: In the uk, for example, you can now expect to the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. Cal use a nd research stud ies. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Imagine printing a human liver. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. Was then transplanted successfully onto a mouse. Maggie fox via nbc news ). One day this will be possible, and with a desperate global shortage of organs for transplant, the medical industry is like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered for example, according to the national foundation for transplants, a standard kidney transplant can on average costs upwards of $300,000, whereas a. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced.
3D-Printed Kidneys Could Shorten Transplant Waiting Times ... : The Test Proved That The 3D Printed Human Liver Tissue Was Stable And Performed Well Tissue Functions Until The Patient Was Able To Receive Liver Transplants.
University research leads to breakthroughs in 3D printed .... Cal use a nd research stud ies. Imagine printing a human liver. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of. Wfirm's 3d printed living ear and muscle implants have been successful in animal trials (source: No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered for example, according to the national foundation for transplants, a standard kidney transplant can on average costs upwards of $300,000, whereas a. Maggie fox via nbc news ). One day this will be possible, and with a desperate global shortage of organs for transplant, the medical industry is like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like a conventional 3d printer would do. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. In the uk, for example, you can now expect to the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. Was then transplanted successfully onto a mouse.
