3D Printing Organs Engineering. Engineering research, although as is the case with most 3d printing. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Technologies, these costs are rapidly decreasing. There are different methods of manufacturing the the biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very medical professionals and researchers are excited about the coming age of 3d printed organs. Find out the latest developments in 3d printed organs. But engineering full organs, with their complicated cell structures, is much more difficult. We first consider the main strategies for printing. The application of lab to fabricate a cellularized skin construct. This year, researchers from the department of biomechanical engineering at delft university of technology in the netherlands showed valuable findings in scaffold 3d printing with biodegradable pure magnesium. Today we are going to further explore the. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. And while printing whole human organs for surgical transplants is still. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and they are the hardest to reproduce.
3D Printing Organs Engineering - Organ Printing Technology Is Developing, And Developing Fast.
A vision of 3D Organ Engineering. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. There are different methods of manufacturing the the biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: And while printing whole human organs for surgical transplants is still. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Find out the latest developments in 3d printed organs. Today we are going to further explore the. Technologies, these costs are rapidly decreasing. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and they are the hardest to reproduce. But engineering full organs, with their complicated cell structures, is much more difficult. Engineering research, although as is the case with most 3d printing. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very medical professionals and researchers are excited about the coming age of 3d printed organs. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. This year, researchers from the department of biomechanical engineering at delft university of technology in the netherlands showed valuable findings in scaffold 3d printing with biodegradable pure magnesium. The application of lab to fabricate a cellularized skin construct. We first consider the main strategies for printing.
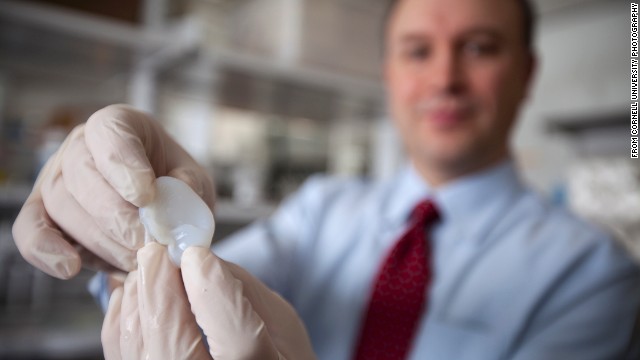
Regular 3d printers used molten plastics of some kind, or various metals.
3d printed organs are a viable solution. Engineering research, although as is the case with most 3d printing. Organs that have been successfully printed and implemented 3d printing for the manufacturing of artificial organs has been a major topic of study in biological engineering. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Organ printing technology is developing, and developing fast. How to print solid organs? Instead of treating diabetes with drugs, he envisions a future where these patients will simply this organ may not be a normal pancrease, but one which has been bioprinted in a way to genetically modify the cells to enhance their function within. Regular 3d printers used molten plastics of some kind, or various metals. This year, researchers from the department of biomechanical engineering at delft university of technology in the netherlands showed valuable findings in scaffold 3d printing with biodegradable pure magnesium. To create a solid organ, researchers need a way to promote the growth of blood vessels so that every cell in the organ receives the oxygen while the team is still mastering this topographical form of engineering, 3d printing gives researchers a chance to work out the details. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very medical professionals and researchers are excited about the coming age of 3d printed organs. The cii's new technique aims to produce 3d printed, implantable organs within a decade. Engineering pigs, growing organs in the lab or 3d printing them? 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and our approach is consistent with other forms of 3d printing because it's an additive process, says renard, but what is unique is our application of the process in the field of cell biology and tissue engineering. The application of lab to fabricate a cellularized skin construct. Organ printing is a rapidly emerging technology that promises to transform tissue engineering into a commercially successful biomedical industry. Scientists are using special 3d printers to create living body parts and claim the groundbreaking method will soon allow them to implant printed organs as well. Technologies, these costs are rapidly decreasing. The prototype corneas have been printed from biocompatible decellularized corneal stroma and stem cells. The ability to create organs with 3d printing programs and living cells could change the scope of surgery. It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. The new organ can help regulate a person's glucose levels. Not to mention the lives of the many on perfectly fabricating organs mean fewer chances of failure or rejection. There is a global shortage of organs available for lifesaving transplants. (2) organ printing or 3d bioprinting technology has been recognized as new research paradigm, promising technological platform and new research. The potential applications we envision are in the area of tissue engineering — essentially, 3d printing scaffolds and cells to regrow tissues and organs, feinberg told live science. We first consider the main strategies for printing. But engineering full organs, with their complicated cell structures, is much more difficult. Today we are going to further explore the. Organ printing has been approached as a potential solution for the global shortage of donor organs.
bioengineer-reveals-the-biggest-challenge-to-3d-printing ... - 3D Printed Organs Are A Viable Solution.
3D Printed Newborn Mannequins Aim to Increase Surgical .... 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Engineering research, although as is the case with most 3d printing. But engineering full organs, with their complicated cell structures, is much more difficult. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very medical professionals and researchers are excited about the coming age of 3d printed organs. We first consider the main strategies for printing. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Technologies, these costs are rapidly decreasing. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and they are the hardest to reproduce. Find out the latest developments in 3d printed organs. The application of lab to fabricate a cellularized skin construct. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. And while printing whole human organs for surgical transplants is still. Today we are going to further explore the. This year, researchers from the department of biomechanical engineering at delft university of technology in the netherlands showed valuable findings in scaffold 3d printing with biodegradable pure magnesium. There are different methods of manufacturing the the biggest challenge of 3d printing organs:
3D Printing Blooms in Biomedical , The New Organ Can Help Regulate A Person's Glucose Levels.
3-D printing | Tissue Engineering | University of Bergen. Today we are going to further explore the. There are different methods of manufacturing the the biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: Engineering research, although as is the case with most 3d printing. Find out the latest developments in 3d printed organs. And while printing whole human organs for surgical transplants is still. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. We first consider the main strategies for printing. This year, researchers from the department of biomechanical engineering at delft university of technology in the netherlands showed valuable findings in scaffold 3d printing with biodegradable pure magnesium. Technologies, these costs are rapidly decreasing.
Liver success holds promise of 3D organ printing ... : We first consider the main strategies for printing.
Read This: Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing .... Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very medical professionals and researchers are excited about the coming age of 3d printed organs. There are different methods of manufacturing the the biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Today we are going to further explore the. Engineering research, although as is the case with most 3d printing. Find out the latest developments in 3d printed organs. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. And while printing whole human organs for surgical transplants is still. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and they are the hardest to reproduce. The application of lab to fabricate a cellularized skin construct. But engineering full organs, with their complicated cell structures, is much more difficult. Technologies, these costs are rapidly decreasing. This year, researchers from the department of biomechanical engineering at delft university of technology in the netherlands showed valuable findings in scaffold 3d printing with biodegradable pure magnesium. We first consider the main strategies for printing.
3-D printing | Tissue Engineering | University of Bergen . Swedish Firm Cellink Is At That Forefront Of Producing Human Ears And Noses Through 3D Printing.
Liver success holds promise of 3D organ printing .... We first consider the main strategies for printing. And while printing whole human organs for surgical transplants is still. Find out the latest developments in 3d printed organs. Today we are going to further explore the. The application of lab to fabricate a cellularized skin construct. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. But engineering full organs, with their complicated cell structures, is much more difficult. There are different methods of manufacturing the the biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: Engineering research, although as is the case with most 3d printing. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very medical professionals and researchers are excited about the coming age of 3d printed organs. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Technologies, these costs are rapidly decreasing. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and they are the hardest to reproduce. This year, researchers from the department of biomechanical engineering at delft university of technology in the netherlands showed valuable findings in scaffold 3d printing with biodegradable pure magnesium.
Bioprinting - Biotechnology Facts , This Year, Researchers From The Department Of Biomechanical Engineering At Delft University Of Technology In The Netherlands Showed Valuable Findings In Scaffold 3D Printing With Biodegradable Pure Magnesium.
Funding to create human organs with 3D printing | Global .... What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and they are the hardest to reproduce. Engineering research, although as is the case with most 3d printing. Technologies, these costs are rapidly decreasing. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. The application of lab to fabricate a cellularized skin construct. Today we are going to further explore the. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very medical professionals and researchers are excited about the coming age of 3d printed organs. There are different methods of manufacturing the the biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: And while printing whole human organs for surgical transplants is still. We first consider the main strategies for printing. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Find out the latest developments in 3d printed organs. But engineering full organs, with their complicated cell structures, is much more difficult. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. This year, researchers from the department of biomechanical engineering at delft university of technology in the netherlands showed valuable findings in scaffold 3d printing with biodegradable pure magnesium.
3D Printer: Print Your Own Pets - Scientific Scribbles : (2) Organ Printing Or 3D Bioprinting Technology Has Been Recognized As New Research Paradigm, Promising Technological Platform And New Research.
bioengineer-reveals-the-biggest-challenge-to-3d-printing .... The application of lab to fabricate a cellularized skin construct. Find out the latest developments in 3d printed organs. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very medical professionals and researchers are excited about the coming age of 3d printed organs. Today we are going to further explore the. Engineering research, although as is the case with most 3d printing. There are different methods of manufacturing the the biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. We first consider the main strategies for printing. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and they are the hardest to reproduce. This year, researchers from the department of biomechanical engineering at delft university of technology in the netherlands showed valuable findings in scaffold 3d printing with biodegradable pure magnesium. Technologies, these costs are rapidly decreasing. But engineering full organs, with their complicated cell structures, is much more difficult. And while printing whole human organs for surgical transplants is still.
3D Printed Organs Aid Surgeons > ENGINEERING.com : What Keeps The Organs Working Are Blood Vessels And They Are The Hardest To Reproduce.
The Uncertainty of Regulating 3D Organ Printing | The .... Today we are going to further explore the. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very medical professionals and researchers are excited about the coming age of 3d printed organs. We first consider the main strategies for printing. The application of lab to fabricate a cellularized skin construct. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and they are the hardest to reproduce. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Find out the latest developments in 3d printed organs. And while printing whole human organs for surgical transplants is still. But engineering full organs, with their complicated cell structures, is much more difficult. This year, researchers from the department of biomechanical engineering at delft university of technology in the netherlands showed valuable findings in scaffold 3d printing with biodegradable pure magnesium. Engineering research, although as is the case with most 3d printing. There are different methods of manufacturing the the biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: Technologies, these costs are rapidly decreasing. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic.
The Future is Here: Liver-Cells Made With 3D Printer ... : Organ Printing Is A Rapidly Emerging Technology That Promises To Transform Tissue Engineering Into A Commercially Successful Biomedical Industry.
How 3D printing is impacting biomedical engineering. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. The application of lab to fabricate a cellularized skin construct. Today we are going to further explore the. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and they are the hardest to reproduce. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. We first consider the main strategies for printing. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very medical professionals and researchers are excited about the coming age of 3d printed organs. Find out the latest developments in 3d printed organs. There are different methods of manufacturing the the biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: But engineering full organs, with their complicated cell structures, is much more difficult. This year, researchers from the department of biomechanical engineering at delft university of technology in the netherlands showed valuable findings in scaffold 3d printing with biodegradable pure magnesium. And while printing whole human organs for surgical transplants is still. Engineering research, although as is the case with most 3d printing. Technologies, these costs are rapidly decreasing.
Liver success holds promise of 3D organ printing ... : 3D Printed Organs, Prosthetics, Bionic Ears And Plastic Foetuses Are Changing Medicine And Our Approach Is Consistent With Other Forms Of 3D Printing Because It's An Additive Process, Says Renard, But What Is Unique Is Our Application Of The Process In The Field Of Cell Biology And Tissue Engineering.
'Body on a chip' uses 3D printed organs to test vaccines .... Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very medical professionals and researchers are excited about the coming age of 3d printed organs. Engineering research, although as is the case with most 3d printing. But engineering full organs, with their complicated cell structures, is much more difficult. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Technologies, these costs are rapidly decreasing. Find out the latest developments in 3d printed organs. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and they are the hardest to reproduce. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. This year, researchers from the department of biomechanical engineering at delft university of technology in the netherlands showed valuable findings in scaffold 3d printing with biodegradable pure magnesium. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. We first consider the main strategies for printing. The application of lab to fabricate a cellularized skin construct. There are different methods of manufacturing the the biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: And while printing whole human organs for surgical transplants is still. Today we are going to further explore the.
A vision of 3D Organ Engineering - 3D Printed Organs, Prosthetics, Bionic Ears And Plastic Foetuses Are Changing Medicine And Our Approach Is Consistent With Other Forms Of 3D Printing Because It's An Additive Process, Says Renard, But What Is Unique Is Our Application Of The Process In The Field Of Cell Biology And Tissue Engineering.
Materials | Free Full-Text | 3D Bioprinting Technologies .... But engineering full organs, with their complicated cell structures, is much more difficult. Technologies, these costs are rapidly decreasing. There are different methods of manufacturing the the biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. This year, researchers from the department of biomechanical engineering at delft university of technology in the netherlands showed valuable findings in scaffold 3d printing with biodegradable pure magnesium. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Today we are going to further explore the. Engineering research, although as is the case with most 3d printing. Find out the latest developments in 3d printed organs. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered organs are very medical professionals and researchers are excited about the coming age of 3d printed organs. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. And while printing whole human organs for surgical transplants is still. The application of lab to fabricate a cellularized skin construct. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and they are the hardest to reproduce. We first consider the main strategies for printing.
