3D Printing Organs And Tissue. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. Imagine printing a human liver. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Explore the science of bioprinting, a type of 3d printing that uses bioink, a printable material that contains living cells. It's the biological materials causing 3d medical printers for artificial tissue are similar in concept to other types of 3d printers. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Organ printing technology is developing, and developing fast. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two dimensional layers of tissues simultaneously. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced.
3D Printing Organs And Tissue : Explore The Science Of Bioprinting, A Type Of 3D Printing That Uses Bioink, A Printable Material That Contains Living Cells.
Collplant. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two dimensional layers of tissues simultaneously. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. Explore the science of bioprinting, a type of 3d printing that uses bioink, a printable material that contains living cells. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. Organ printing technology is developing, and developing fast. It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; It's the biological materials causing 3d medical printers for artificial tissue are similar in concept to other types of 3d printers. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Imagine printing a human liver. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is.
Estimates for a date when organ bioprinting will be.
The future is created in the present, and bioprinting will change the future of medicine. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two dimensional layers of tissues simultaneously. 3dprinting.com will keep you informed of the latest developments in the bio printing industry. After implanted, this airway splint expanded automatically under the thermal stimuli from the internal warm organ, which leaves growing space for malacia airway. There has been a lot of buzz around 3d printing organs but many are still left to wonder, how does bio 3d printing work and is the technology at the point where we can you might be surprised to hear that the process for printing organs and other living tissue is incredibly similar to most fdm machines. 3d bioprinting of tissue and organs. Estimates for a date when organ bioprinting will be. Bioinks can then be 3d bioprinted into functional tissue constructs for drug screening, disease modeling, and in vitro transplantation. I am amazed about the technology advancement in organs and tissues. Therefore, the prostate model can aid medical professionals to perform more effective preoperative planning and rehearsal and predict. Now we can print organs and purchase a 3d printer for home use on small projects. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Explore the science of bioprinting, a type of 3d printing that uses bioink, a printable material that contains living cells. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. 3d printing technologies for tissue engineering. The remaining, still liquid hydrogel is washed out after the printing in addition, the resolution of the method, around 300 micrometers, is far too low to reproduce the delicate structures of natural tissue. 3d printing is now set to revolutionise the medical industry, especially in regenerative medicine, as it enables cells, tissues and organs to be printed on whilst 3d bioprinting of living tissue still requires the cells to be cultured and grow, the printing process provides a new approach to fabricating. Imagine printing a human liver. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. Nowadays scientists are in the midst of moving from printing tiny sheets of tissue to entire 3d organs. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. The 3d printed prostate model demonstrated high fidelity with patient organ and tissue in anatomical, static and dynamic mechanical, hardness, and optical properties. It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; Organ printing technology is now one of potentially superior strategies or emerging technological platforms for organ level tissue engineering (rustad in several countries, thesis on different aspects of biofabrication, 3d bioprinting and organ printing have been already prepared and successfully. The future is created in the present, and bioprinting will change the future of medicine. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Hard tissues and organs, including the bones, teeth and cartilage, are the most extensively exploited and rapidly developed areas in regenerative medicine field. Bioinks are created by combining cultured cells and various biocompatable materials.
Materials | Free Full-Text | 3D Bioprinting Technologies ... - The 3D Printed Prostate Model Demonstrated High Fidelity With Patient Organ And Tissue In Anatomical, Static And Dynamic Mechanical, Hardness, And Optical Properties.
3D Bioprinting Of Tissues And Organs Brings Life To .... When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. Organ printing technology is developing, and developing fast. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two dimensional layers of tissues simultaneously. Explore the science of bioprinting, a type of 3d printing that uses bioink, a printable material that contains living cells. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. It's the biological materials causing 3d medical printers for artificial tissue are similar in concept to other types of 3d printers. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. Imagine printing a human liver. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced.
Revolution: 3D printed heart with human tissue : It's Not The Mechanical Process That's The Problem Here;
The Future is Now! A Full List of Organs You Can 3D Print .... 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Imagine printing a human liver. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two dimensional layers of tissues simultaneously. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic.
Scientists Can Now 3D Print Functional Organs - YouTube . Now we can print organs and purchase a 3d printer for home use on small projects.
3D Printers Could be Banned by 2016 for Bioprinting Human .... The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. It's the biological materials causing 3d medical printers for artificial tissue are similar in concept to other types of 3d printers. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two dimensional layers of tissues simultaneously. Explore the science of bioprinting, a type of 3d printing that uses bioink, a printable material that contains living cells. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. Imagine printing a human liver. Organ printing technology is developing, and developing fast. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs.
bioengineer-reveals-the-biggest-challenge-to-3d-printing ... , However, The Technology Still Has A Ways To Go Before It Is.
Materials | Free Full-Text | 3D Bioprinting Technologies .... When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Imagine printing a human liver. Explore the science of bioprinting, a type of 3d printing that uses bioink, a printable material that contains living cells. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two dimensional layers of tissues simultaneously. Organ printing technology is developing, and developing fast. It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. It's the biological materials causing 3d medical printers for artificial tissue are similar in concept to other types of 3d printers. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least.
3D Human Organ Printing - Bioprinting . However, The Technology Still Has A Ways To Go Before It Is.
Bioprinting Gets a Boost from Thick 3D Printed Human .... It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Imagine printing a human liver. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two dimensional layers of tissues simultaneously. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. Organ printing technology is developing, and developing fast. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Explore the science of bioprinting, a type of 3d printing that uses bioink, a printable material that contains living cells. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. It's the biological materials causing 3d medical printers for artificial tissue are similar in concept to other types of 3d printers. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation.
organovo-bioprinter-3d-printer-tissue-human-organ-3 ... - 3D Bioprinting Of Tissue And Organs.
The Future is Now! A Full List of Organs You Can 3D Print. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; It's the biological materials causing 3d medical printers for artificial tissue are similar in concept to other types of 3d printers. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Imagine printing a human liver. Organ printing technology is developing, and developing fast. Explore the science of bioprinting, a type of 3d printing that uses bioink, a printable material that contains living cells. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two dimensional layers of tissues simultaneously. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues.
3D Printing Organs Heading Toward Future Of Indestructible ... - The Remaining, Still Liquid Hydrogel Is Washed Out After The Printing In Addition, The Resolution Of The Method, Around 300 Micrometers, Is Far Too Low To Reproduce The Delicate Structures Of Natural Tissue.
What is the future of 3D printed organs? (2020 Update). Organ printing technology is developing, and developing fast. It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Imagine printing a human liver. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two dimensional layers of tissues simultaneously. It's the biological materials causing 3d medical printers for artificial tissue are similar in concept to other types of 3d printers. Explore the science of bioprinting, a type of 3d printing that uses bioink, a printable material that contains living cells. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues.
Future of regenerative medicine may be making human tissue ... - Over The Last Two Decades, A Wide Variety Of 3D Printing Technologies Have Been Adapted To Hard Tissue And Organ Engineering.
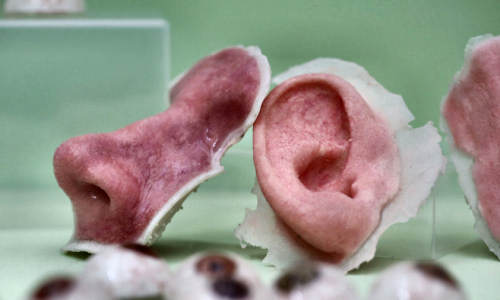
Need a new ear? Technion opens 3D tissue printer for .... It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; It's the biological materials causing 3d medical printers for artificial tissue are similar in concept to other types of 3d printers. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Explore the science of bioprinting, a type of 3d printing that uses bioink, a printable material that contains living cells. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Organ printing technology is developing, and developing fast. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. Imagine printing a human liver. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two dimensional layers of tissues simultaneously. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic.
3D Printing | Stock Discussion Forums , Hard Tissues And Organs, Including The Bones, Teeth And Cartilage, Are The Most Extensively Exploited And Rapidly Developed Areas In Regenerative Medicine Field.
3D Printing Myths? Find Out Whats True And What's Not .... No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two dimensional layers of tissues simultaneously. It's the biological materials causing 3d medical printers for artificial tissue are similar in concept to other types of 3d printers. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. Explore the science of bioprinting, a type of 3d printing that uses bioink, a printable material that contains living cells. Imagine printing a human liver. Organ printing technology is developing, and developing fast. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least.
organovo-bioprinter-3d-printer-tissue-human-organ-3 ... - Printing Tiny Organs For 'Body On A Chip'].
Israeli firm seeking breakthrough in 3D organ printing .... It's not the mechanical process that's the problem here; The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable organovo is perhaps the most prominent company conducting research into the 3d bioprinting process for live tissues and 3d printed organs, at least. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two dimensional layers of tissues simultaneously. Organ printing technology is developing, and developing fast. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. It's the biological materials causing 3d medical printers for artificial tissue are similar in concept to other types of 3d printers. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Explore the science of bioprinting, a type of 3d printing that uses bioink, a printable material that contains living cells. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Imagine printing a human liver. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs.
