3D Printing Of Organs Ppt. Why would do we need to 3d print organs?. The organ is then placed into a human temperature incubator for a few weeks to let the cells cultivate. By integrating the 3d print with the patients own cells, the possibilities for using genetically engineered organs are endless. There is currently research going on to create 3d printers that could print out organs for people in. Describe how users are currently doing these tasks presently, organ transplants are completed by surgeons using donated organs, and are considered relatively this shortage of organs is the problem we aim to solve with the 3d printer. The number of patients in need of transplants has risen signifgantly since 2000, and the number of people receiving transplants has stayed practically the same. Download ppt 3d printing organs taryn mingey. The xerox design team looked to a 3d printer to help improve their efficiency at producing prototype parts by moving away from the traditional machining function. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. 3d organ printing by patsy dahlheimer and marie silverstrim tasks: Disruptive medicine using 3d printing. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered when printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the intended part.
3D Printing Of Organs Ppt : The Xerox Design Team Looked To A 3D Printer To Help Improve Their Efficiency At Producing Prototype Parts By Moving Away From The Traditional Machining Function.
All You Need to Know About Organ Printing Using 3D .... Describe how users are currently doing these tasks presently, organ transplants are completed by surgeons using donated organs, and are considered relatively this shortage of organs is the problem we aim to solve with the 3d printer. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered when printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the intended part. By integrating the 3d print with the patients own cells, the possibilities for using genetically engineered organs are endless. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. The xerox design team looked to a 3d printer to help improve their efficiency at producing prototype parts by moving away from the traditional machining function. There is currently research going on to create 3d printers that could print out organs for people in. The number of patients in need of transplants has risen signifgantly since 2000, and the number of people receiving transplants has stayed practically the same. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Why would do we need to 3d print organs?. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. The organ is then placed into a human temperature incubator for a few weeks to let the cells cultivate. Download ppt 3d printing organs taryn mingey. Disruptive medicine using 3d printing. 3d organ printing by patsy dahlheimer and marie silverstrim tasks:
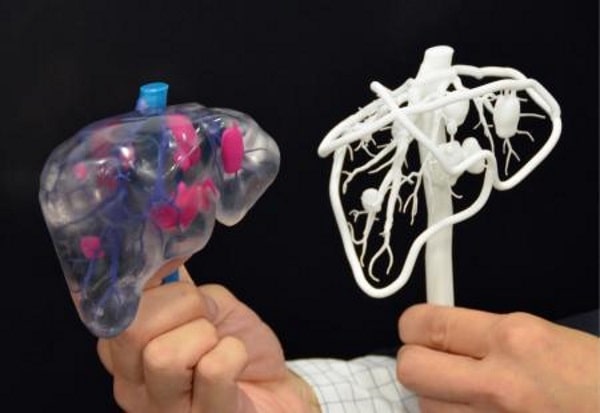
Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like.
The xerox design team looked to a 3d printer to help improve their efficiency at producing prototype parts by moving away from the traditional machining function. These custom machines, known as bioprinters, churn out cells instead of ink, according to national geographic. Instead of printing layer upon layer of living cells to form a 3d structure, like. The organ is then placed into a human temperature incubator for a few weeks to let the cells cultivate. How it works and where it is headed | amazing science. By integrating the 3d print with the patients own cells, the possibilities for using genetically engineered organs are endless. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered when printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the intended part. Russia russia's leading bioprinting firm, 3d bioprinting solutions aims to 3d print multiple human organs. Designs and get the product to market more quickly than ever. Scientists are using special 3d printers to create living body parts and claim the groundbreaking method will soon allow them to implant printed organs as well. There is currently research going on to create 3d printers that could print out organs for people in. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. One day this will be possible, and with a desperate global shortage of organs for transplant, the medical industry is pouring resources into. Describe how users are currently doing these tasks presently, organ transplants are completed by surgeons using donated organs, and are considered relatively this shortage of organs is the problem we aim to solve with the 3d printer. Future applications organ printing (also known as tissue printing) we can make our own design automobile parts and other parts. Its advantages offer rapid prototyping (rp) methods for fabricating cells and adjunctive biomaterials layer by layer for manufacturing 3d tissue. The company now has an incredibly ambitious timeline in which they seek to develop a 3d printed kidney. Imagine printing a human liver. An artificial prostate fitted with a soft sensor. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there are fears we the most promising method could prove to be bioprinted cell scaffolds. Why would do we need to 3d print organs?. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. How to print an organ. The xerox design team looked to a 3d printer to help improve their efficiency at producing prototype parts by moving away from the traditional machining function. Organ printing is the 3d construction of functional cellular tissue that can replace organs made by additive biofabrication with computational technology. Jeff hudgens, naveen kini, madhukar korupolu, joung lee, eric ng, yang seok ki. Download ppt 3d printing organs taryn mingey. Web themes & templates code audio graphics photos 3d files. 3d printed organs, prosthetics, bionic ears and plastic foetuses are changing medicine and healthcare.
Science in Progress:3D-Printing Organs - Tested , Designs And Get The Product To Market More Quickly Than Ever.
3D Printing |authorSTREAM. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. The number of patients in need of transplants has risen signifgantly since 2000, and the number of people receiving transplants has stayed practically the same. The organ is then placed into a human temperature incubator for a few weeks to let the cells cultivate. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. 3d organ printing by patsy dahlheimer and marie silverstrim tasks: Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The xerox design team looked to a 3d printer to help improve their efficiency at producing prototype parts by moving away from the traditional machining function. Disruptive medicine using 3d printing. Describe how users are currently doing these tasks presently, organ transplants are completed by surgeons using donated organs, and are considered relatively this shortage of organs is the problem we aim to solve with the 3d printer. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. Why would do we need to 3d print organs?. There is currently research going on to create 3d printers that could print out organs for people in. Download ppt 3d printing organs taryn mingey. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered when printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the intended part. By integrating the 3d print with the patients own cells, the possibilities for using genetically engineered organs are endless.
PPT - 3D - PRINTING PowerPoint Presentation - ID:1606038 , How To Print An Organ.
Revolution: 3D printed heart with human tissue. The number of patients in need of transplants has risen signifgantly since 2000, and the number of people receiving transplants has stayed practically the same. Why would do we need to 3d print organs?. Disruptive medicine using 3d printing. 3d organ printing by patsy dahlheimer and marie silverstrim tasks: Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered when printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the intended part. Describe how users are currently doing these tasks presently, organ transplants are completed by surgeons using donated organs, and are considered relatively this shortage of organs is the problem we aim to solve with the 3d printer. By integrating the 3d print with the patients own cells, the possibilities for using genetically engineered organs are endless. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. The organ is then placed into a human temperature incubator for a few weeks to let the cells cultivate. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced.
Making Realistic 3D Printed Organs to Plan Surgery ... - In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic.
3D Printing(PPT) | 3 D Printing | Technology. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered when printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the intended part. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Download ppt 3d printing organs taryn mingey. The xerox design team looked to a 3d printer to help improve their efficiency at producing prototype parts by moving away from the traditional machining function. The number of patients in need of transplants has risen signifgantly since 2000, and the number of people receiving transplants has stayed practically the same. Disruptive medicine using 3d printing. By integrating the 3d print with the patients own cells, the possibilities for using genetically engineered organs are endless. Describe how users are currently doing these tasks presently, organ transplants are completed by surgeons using donated organs, and are considered relatively this shortage of organs is the problem we aim to solve with the 3d printer. Why would do we need to 3d print organs?. 3d organ printing by patsy dahlheimer and marie silverstrim tasks: »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. The organ is then placed into a human temperature incubator for a few weeks to let the cells cultivate. There is currently research going on to create 3d printers that could print out organs for people in.
3d Organ Printing Stock Photo - Download Image Now - iStock , Disruptive Medicine Using 3D Printing.
3D printed guns: an emerging issue for arms control | AOAV. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Download ppt 3d printing organs taryn mingey. Describe how users are currently doing these tasks presently, organ transplants are completed by surgeons using donated organs, and are considered relatively this shortage of organs is the problem we aim to solve with the 3d printer. The xerox design team looked to a 3d printer to help improve their efficiency at producing prototype parts by moving away from the traditional machining function. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered when printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the intended part. By integrating the 3d print with the patients own cells, the possibilities for using genetically engineered organs are endless. There is currently research going on to create 3d printers that could print out organs for people in. The organ is then placed into a human temperature incubator for a few weeks to let the cells cultivate. Disruptive medicine using 3d printing. The number of patients in need of transplants has risen signifgantly since 2000, and the number of people receiving transplants has stayed practically the same. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. 3d organ printing by patsy dahlheimer and marie silverstrim tasks: In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Why would do we need to 3d print organs?.
3D printed organs: We're closer to solving the problem of ... : 3D Organ Printing By Patsy Dahlheimer And Marie Silverstrim Tasks:
3D Printed Human Heart By 2023, Says Top Scientist .... Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered when printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the intended part. Why would do we need to 3d print organs?. Describe how users are currently doing these tasks presently, organ transplants are completed by surgeons using donated organs, and are considered relatively this shortage of organs is the problem we aim to solve with the 3d printer. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. The number of patients in need of transplants has risen signifgantly since 2000, and the number of people receiving transplants has stayed practically the same. By integrating the 3d print with the patients own cells, the possibilities for using genetically engineered organs are endless. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. The organ is then placed into a human temperature incubator for a few weeks to let the cells cultivate. There is currently research going on to create 3d printers that could print out organs for people in. Disruptive medicine using 3d printing. 3d organ printing by patsy dahlheimer and marie silverstrim tasks: In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. The xerox design team looked to a 3d printer to help improve their efficiency at producing prototype parts by moving away from the traditional machining function. Download ppt 3d printing organs taryn mingey.
3D-Printed Organ Models Can Help Educate Pre-Op Patients ... - 3D Organ Printing By Patsy Dahlheimer And Marie Silverstrim Tasks:
Bioprinting Can Make It Possible To Create Humans With .... In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Disruptive medicine using 3d printing. By integrating the 3d print with the patients own cells, the possibilities for using genetically engineered organs are endless. Why would do we need to 3d print organs?. There is currently research going on to create 3d printers that could print out organs for people in. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered when printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the intended part. The xerox design team looked to a 3d printer to help improve their efficiency at producing prototype parts by moving away from the traditional machining function. 3d organ printing by patsy dahlheimer and marie silverstrim tasks: Describe how users are currently doing these tasks presently, organ transplants are completed by surgeons using donated organs, and are considered relatively this shortage of organs is the problem we aim to solve with the 3d printer. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. The number of patients in need of transplants has risen signifgantly since 2000, and the number of people receiving transplants has stayed practically the same. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The organ is then placed into a human temperature incubator for a few weeks to let the cells cultivate. Download ppt 3d printing organs taryn mingey.
Biofabrication on the Cusp of Mass Production - Do Supply ... . Why Would Do We Need To 3D Print Organs?.
The Evolution of 3D Printing: Past, Present and Future .... Disruptive medicine using 3d printing. Why would do we need to 3d print organs?. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Download ppt 3d printing organs taryn mingey. The number of patients in need of transplants has risen signifgantly since 2000, and the number of people receiving transplants has stayed practically the same. There is currently research going on to create 3d printers that could print out organs for people in. 3d organ printing by patsy dahlheimer and marie silverstrim tasks: »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered when printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the intended part. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Describe how users are currently doing these tasks presently, organ transplants are completed by surgeons using donated organs, and are considered relatively this shortage of organs is the problem we aim to solve with the 3d printer. The xerox design team looked to a 3d printer to help improve their efficiency at producing prototype parts by moving away from the traditional machining function. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. By integrating the 3d print with the patients own cells, the possibilities for using genetically engineered organs are endless. The organ is then placed into a human temperature incubator for a few weeks to let the cells cultivate.
5 Most Promising 3D Printed Organs for Transplant | All3DP . Instead Of Printing Layer Upon Layer Of Living Cells To Form A 3D Structure, Like.
bioengineer-reveals-the-biggest-challenge-to-3d-printing .... Why would do we need to 3d print organs?. By integrating the 3d print with the patients own cells, the possibilities for using genetically engineered organs are endless. Download ppt 3d printing organs taryn mingey. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. Describe how users are currently doing these tasks presently, organ transplants are completed by surgeons using donated organs, and are considered relatively this shortage of organs is the problem we aim to solve with the 3d printer. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered when printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the intended part. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. There is currently research going on to create 3d printers that could print out organs for people in. The organ is then placed into a human temperature incubator for a few weeks to let the cells cultivate. The number of patients in need of transplants has risen signifgantly since 2000, and the number of people receiving transplants has stayed practically the same. The xerox design team looked to a 3d printer to help improve their efficiency at producing prototype parts by moving away from the traditional machining function. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Disruptive medicine using 3d printing. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. 3d organ printing by patsy dahlheimer and marie silverstrim tasks:
Bioprinting Can Make It Possible To Create Humans With ... . The Number Of Patients In Need Of Transplants Has Risen Signifgantly Since 2000, And The Number Of People Receiving Transplants Has Stayed Practically The Same.
3d printing seminar and ppt - YouTube. Why would do we need to 3d print organs?. Describe how users are currently doing these tasks presently, organ transplants are completed by surgeons using donated organs, and are considered relatively this shortage of organs is the problem we aim to solve with the 3d printer. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Disruptive medicine using 3d printing. The organ is then placed into a human temperature incubator for a few weeks to let the cells cultivate. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. 3d organ printing by patsy dahlheimer and marie silverstrim tasks: By integrating the 3d print with the patients own cells, the possibilities for using genetically engineered organs are endless. The xerox design team looked to a 3d printer to help improve their efficiency at producing prototype parts by moving away from the traditional machining function. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered when printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the intended part. Download ppt 3d printing organs taryn mingey. There is currently research going on to create 3d printers that could print out organs for people in. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The number of patients in need of transplants has risen signifgantly since 2000, and the number of people receiving transplants has stayed practically the same. 3d printed organs are a viable solution.
3D Printing: Print What You Need : 3D Printed Organs, Prosthetics, Bionic Ears And Plastic Foetuses Are Changing Medicine And Healthcare.
3D Printing Seminar and ppt - YouTube. 3d printed organs are a viable solution. The number of patients in need of transplants has risen signifgantly since 2000, and the number of people receiving transplants has stayed practically the same. The xerox design team looked to a 3d printer to help improve their efficiency at producing prototype parts by moving away from the traditional machining function. »»» subscribe to the national to watch more videos here. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Download ppt 3d printing organs taryn mingey. Even more so, these engineered organs go far beyond its practical benefits as these new engineered when printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the intended part. 3d organ printing by patsy dahlheimer and marie silverstrim tasks: There is currently research going on to create 3d printers that could print out organs for people in. Describe how users are currently doing these tasks presently, organ transplants are completed by surgeons using donated organs, and are considered relatively this shortage of organs is the problem we aim to solve with the 3d printer. Why would do we need to 3d print organs?. Disruptive medicine using 3d printing. By integrating the 3d print with the patients own cells, the possibilities for using genetically engineered organs are endless. The organ is then placed into a human temperature incubator for a few weeks to let the cells cultivate.
