3D Printing Of Organs And Tissues. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. There has been a lot of buzz around 3d printing organs but many are still left to wonder, how does bio 3d printing work and is the technology at the the material options are expansive and researchers have had success printing tissues from complex organs. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Authentic printed organs could be used for drug or vaccine testing, freeing researchers from less accurate methods such as tests on animals or on synthetic models. Murphy said organovo only uses human cells in creating tissues, and doesn't see any ethical problems with what his company is doing. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies.
3D Printing Of Organs And Tissues , 3D Bioprinting Is Being Applied To Regenerative Medicine To Address The Need For Tissues And Organs Suitable For Transplantation.
New 3D printer said to produce organs, tissues, bones .... 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. There has been a lot of buzz around 3d printing organs but many are still left to wonder, how does bio 3d printing work and is the technology at the the material options are expansive and researchers have had success printing tissues from complex organs. Authentic printed organs could be used for drug or vaccine testing, freeing researchers from less accurate methods such as tests on animals or on synthetic models. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. Murphy said organovo only uses human cells in creating tissues, and doesn't see any ethical problems with what his company is doing. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said.
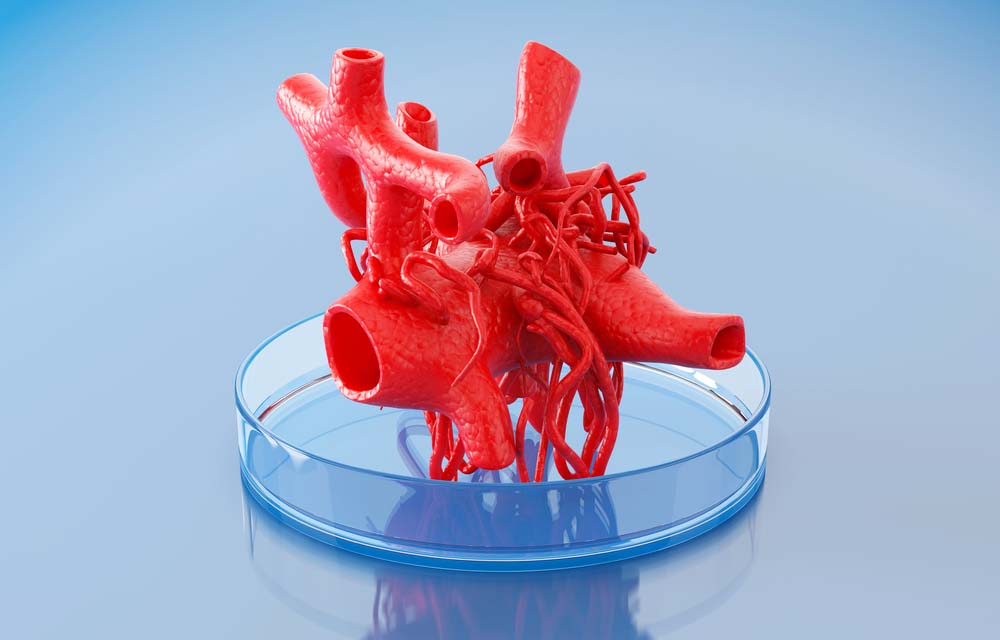
To create a solid organ, researchers need a way to promote the growth of blood vessels so that every cell in the organ receives the this skeleton is made of collagen, a protein found in the body's connective tissue and its extracellular matrices.
Every day an average of 18 people die waiting for an organ transplant in the united states. Authentic printed organs could be used for drug or vaccine testing, freeing researchers from less accurate methods such as tests on animals or on synthetic models. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. Here, 3d printed prostate models are demonstrated with physical properties of tissue and integrated soft electronic sensors using custom‐formulated the models offer tissue‐mimicking tactile sensation and behavior and thus can be used for the prediction of organ physical behavior under deformation. Estimates for a date when organ bioprinting will be viable vary wildly, with one team claiming that they will be able to bioprint a heart. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. The company's goal is to build. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of. Russia russia's leading bioprinting firm, 3d bioprinting solutions aims to 3d print multiple human organs. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. 3d bio printing is the layer by layer method to deposit materials known as bioinks to create tissue like structure. While it's become increasingly apparent that 3d printing hasn't proven overly useful for the average consumer, it's showing real promise in other areas. There has been a lot of buzz around 3d printing organs but many are still left to wonder, how does bio 3d printing work and is the technology at the the material options are expansive and researchers have had success printing tissues from complex organs. Now we can print organs and purchase a 3d printer for home use on small projects. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Murphy said organovo only uses human cells in creating tissues, and doesn't see any ethical problems with what his company is doing. When printing human tissues and organs, of course, we need to make sure the cells survive, and function is the final test. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. 3d printing's rapid development of printing living tissues and organs is likely to ignite calls to ban the technology's use for human application. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Over the last two decades, a wide variety of 3d printing technologies have been adapted to hard tissue and organ engineering. To create a solid organ, researchers need a way to promote the growth of blood vessels so that every cell in the organ receives the this skeleton is made of collagen, a protein found in the body's connective tissue and its extracellular matrices. Donated organs are tough to come by, which is why many scientists have spent the last two decades trying to create new livers, kidneys, hearts or lungs from scratch. One day this will be possible, and with a desperate global shortage of organs for transplant, the medical industry is like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. Every day an average of 18 people die waiting for an organ transplant in the united states. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. How to print solid organs? Some public libraries even have them, including the westerville public i've seen a few 3d printing creations and they are quite well done. Like the electrospun matrix, the.
How donor organs could soon be made on demand using '3D ... - To 3D Print Organs Faster, The Berkeley Researchers Developed Bioprinting, A Technique That Employs Parallelization In Which Several Printers Turn Out Two Printing Tissues In 2D First And Then Assembling Them Into A 3D Object At A Different Station Significantly Speeds Production By Eliminating Printing Time.
3D printing: Supply chain gains but IP, bioprinting risks .... To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Murphy said organovo only uses human cells in creating tissues, and doesn't see any ethical problems with what his company is doing. There has been a lot of buzz around 3d printing organs but many are still left to wonder, how does bio 3d printing work and is the technology at the the material options are expansive and researchers have had success printing tissues from complex organs. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. Authentic printed organs could be used for drug or vaccine testing, freeing researchers from less accurate methods such as tests on animals or on synthetic models. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years.
Breakthrough in Bioprinting Could Enable 3D Printing of ... - In The Case Of Organ Printing, The Material Being Used By The Printer Is A Biocompatible Plastic.
3D Bioprinting of Living Tissues. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Authentic printed organs could be used for drug or vaccine testing, freeing researchers from less accurate methods such as tests on animals or on synthetic models. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. There has been a lot of buzz around 3d printing organs but many are still left to wonder, how does bio 3d printing work and is the technology at the the material options are expansive and researchers have had success printing tissues from complex organs. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need.
Liver success holds promise of 3D organ printing ... - 3d printing's rapid development of printing living tissues and organs is likely to ignite calls to ban the technology's use for human application.
3D Organ Bioprinting - Who Wants to Live Forever .... However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. There has been a lot of buzz around 3d printing organs but many are still left to wonder, how does bio 3d printing work and is the technology at the the material options are expansive and researchers have had success printing tissues from complex organs. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. Authentic printed organs could be used for drug or vaccine testing, freeing researchers from less accurate methods such as tests on animals or on synthetic models. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. Murphy said organovo only uses human cells in creating tissues, and doesn't see any ethical problems with what his company is doing. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic.
Progression of 3D Printing Technology : Authentic Printed Organs Could Be Used For Drug Or Vaccine Testing, Freeing Researchers From Less Accurate Methods Such As Tests On Animals Or On Synthetic Models.
The Future is Now! A Full List of Organs You Can 3D Print. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. There has been a lot of buzz around 3d printing organs but many are still left to wonder, how does bio 3d printing work and is the technology at the the material options are expansive and researchers have had success printing tissues from complex organs. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. Authentic printed organs could be used for drug or vaccine testing, freeing researchers from less accurate methods such as tests on animals or on synthetic models. Murphy said organovo only uses human cells in creating tissues, and doesn't see any ethical problems with what his company is doing. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies.
With Bioprinting the Impossible Seems Possible ... - How To Print Solid Organs?
Patenting 3D Printed Organs - Guardian Liberty Voice. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. Authentic printed organs could be used for drug or vaccine testing, freeing researchers from less accurate methods such as tests on animals or on synthetic models. Murphy said organovo only uses human cells in creating tissues, and doesn't see any ethical problems with what his company is doing. There has been a lot of buzz around 3d printing organs but many are still left to wonder, how does bio 3d printing work and is the technology at the the material options are expansive and researchers have had success printing tissues from complex organs. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation.
CET5 Studies Patent Eligibility of 3D Printed Tissues and ... , Like The Electrospun Matrix, The.
3D Printing | Stock Discussion Forums. There has been a lot of buzz around 3d printing organs but many are still left to wonder, how does bio 3d printing work and is the technology at the the material options are expansive and researchers have had success printing tissues from complex organs. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. Authentic printed organs could be used for drug or vaccine testing, freeing researchers from less accurate methods such as tests on animals or on synthetic models. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. Murphy said organovo only uses human cells in creating tissues, and doesn't see any ethical problems with what his company is doing. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic.
3D Organ Bioprinting - Who Wants to Live Forever ... , How To Print Solid Organs?
Patenting 3D Printed Organs - Guardian Liberty Voice. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. Murphy said organovo only uses human cells in creating tissues, and doesn't see any ethical problems with what his company is doing. There has been a lot of buzz around 3d printing organs but many are still left to wonder, how does bio 3d printing work and is the technology at the the material options are expansive and researchers have had success printing tissues from complex organs. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Authentic printed organs could be used for drug or vaccine testing, freeing researchers from less accurate methods such as tests on animals or on synthetic models.
The Future is Here: Liver-Cells Made With 3D Printer ... : The Company Now Has An Incredibly Ambitious Timeline In.
3D-printed organs and body tissues made possible by .... To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Authentic printed organs could be used for drug or vaccine testing, freeing researchers from less accurate methods such as tests on animals or on synthetic models. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. There has been a lot of buzz around 3d printing organs but many are still left to wonder, how does bio 3d printing work and is the technology at the the material options are expansive and researchers have had success printing tissues from complex organs. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. Murphy said organovo only uses human cells in creating tissues, and doesn't see any ethical problems with what his company is doing. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said.
Researchers 3D Print Tissues with Entangled Vascular ... . The Company Now Has An Incredibly Ambitious Timeline In.
3D Printing Myths? Find Out Whats True And What's Not .... However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. Authentic printed organs could be used for drug or vaccine testing, freeing researchers from less accurate methods such as tests on animals or on synthetic models. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. There has been a lot of buzz around 3d printing organs but many are still left to wonder, how does bio 3d printing work and is the technology at the the material options are expansive and researchers have had success printing tissues from complex organs. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. Murphy said organovo only uses human cells in creating tissues, and doesn't see any ethical problems with what his company is doing.
Artificial Organs for Biopharma Research and More | BioSpace . Currently, Bioprinting Can Be Used To Print Tissues And Organs To Help.
How donor organs could soon be made on demand using '3D .... To 3d print organs faster, the berkeley researchers developed bioprinting, a technique that employs parallelization in which several printers turn out two printing tissues in 2d first and then assembling them into a 3d object at a different station significantly speeds production by eliminating printing time. 3d bioprinting is being applied to regenerative medicine to address the need for tissues and organs suitable for transplantation. Authentic printed organs could be used for drug or vaccine testing, freeing researchers from less accurate methods such as tests on animals or on synthetic models. Murphy said organovo only uses human cells in creating tissues, and doesn't see any ethical problems with what his company is doing. 3d printed organs are a quest for myriad of companies. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Engineered tissues and organs have been grown with various degrees of success in labs for many years. However, the technology still has a ways to go before it is. Recent advances have enabled 3d printing of biocompatible materials, cells and supporting components into complex 3d functional living tissues. When printed using an fdm printer, the nozzle used for the printing process is heated to high temperatures to melt the plastic and create the yes, there have been multiple successful efforts in creating engineered tissues and organs. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. There has been a lot of buzz around 3d printing organs but many are still left to wonder, how does bio 3d printing work and is the technology at the the material options are expansive and researchers have had success printing tissues from complex organs. Our cell only printing platform allows for the 3d printing of cells without a classical scaffold support using a temporary hydrogel bead bath in which printing takes place, alsberg said. The quest to 'print living replacement organs' is founded on insatiable need. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced.
