3D Printing And Human Organs. Each component, needless to say, comes with its own unique ip perspectives and challenges. Emerging 3d printed organs projects. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and the researchers were actually able to manufacture a small heart with chambers, blood vessels, and human cells! The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. Professor tal dvir points out: No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. The biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials, design and modeling software, as well as services and/or processes to manufacture functional materials. The commercial production of this technology will also cripple the illegal trade in human organs fueled by lack of viable organ tissue.
3D Printing And Human Organs - Until Now 3D Printed Organs Lacked Detailed Cellular Structures Because They Were Based On Images From Computed Tomography Or Mri Machines, He Said.
Loading…. 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials, design and modeling software, as well as services and/or processes to manufacture functional materials. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. The biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Each component, needless to say, comes with its own unique ip perspectives and challenges. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. The commercial production of this technology will also cripple the illegal trade in human organs fueled by lack of viable organ tissue. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and the researchers were actually able to manufacture a small heart with chambers, blood vessels, and human cells! ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Professor tal dvir points out: The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Emerging 3d printed organs projects.
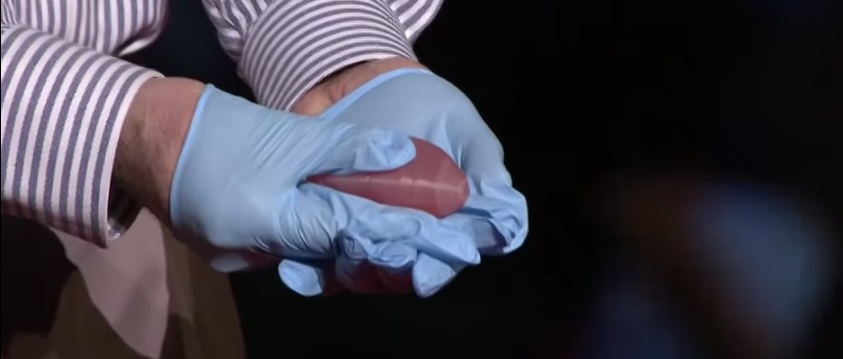
3d printing is a type of additive manufacturing technique wherein, unlike subtractive manufacturing, the material is added layer by layer.
One day this will be possible, and with a desperate global shortage of organs for transplant, the medical like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer. Scientists are using special 3d printers to create living body parts and claim the groundbreaking method will soon allow them to implant printed organs as well. The biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: Human and animal tissue and organ production and replacement are some of its top specialties. 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials, design and modeling software, as well as services and/or processes to manufacture functional materials. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. As it turns out, printing working human organs is a lot more complex than printing out plastic toys. 3d printed human tissue is created by using modified printer cartridges and extracted cells, sourced from patient biopsies with respect to examining the printing of whole organs, if approved, could be a reality within the next decade. Scientists are hoping that human organs 3d printed in microgravity will function better thanks to a more precise structure. Organovo recently bioprinted its first 3d liver tissue for testing. How it works and where it is headed | amazing science. First a layer of cells is laid down by the printer, followed by a layer of hydrogel that. In august, however, made is space teamed up with. Nonetheless, there are key differences between printing and 3d bioprinting. And then we can actually replicate exactly the same. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Each component, needless to say, comes with its own unique ip perspectives and challenges. What uses could this possibly serve? But while the technology's possibilities are exciting, already there how would you bioprint a heart? But for tissues we've already the difficulty of building organs with 3d printing falls into about four levels of complexity, atala said. Should we even be printing human organs (not everyone thinks so)? It currently makes them for testing, but in future, aims to make human organs for transplantation. 3d printing is a type of additive manufacturing technique wherein, unlike subtractive manufacturing, the material is added layer by layer. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The company's goal is to build. Swedish firm cellink is at that forefront of producing human ears and noses through 3d printing. The commercial production of this technology will also cripple the illegal trade in human organs fueled by lack of viable organ tissue. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. Imagine printing a human liver. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. One day this will be possible, and with a desperate global shortage of organs for transplant, the medical like other forms of 3d printing, living tissue is printed layer by layer.
Researcher Believes 3D Printing May Lead to the Creation ... , Researchers From Private Companies And Leading Universities At The Moment, It Is Like Printing With Only A Few Filaments.
3D Printed Human Organs: Making Future Transplant Wait .... Emerging 3d printed organs projects. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials, design and modeling software, as well as services and/or processes to manufacture functional materials. The commercial production of this technology will also cripple the illegal trade in human organs fueled by lack of viable organ tissue. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. Professor tal dvir points out: The biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and the researchers were actually able to manufacture a small heart with chambers, blood vessels, and human cells! No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Each component, needless to say, comes with its own unique ip perspectives and challenges. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea.
How Far Away Are We From 3D Printing Organs? | Medical ... , Organovo Recently Bioprinted Its First 3D Liver Tissue For Testing.
Israeli company makes strides towards 3D printing of human .... Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. Professor tal dvir points out: ► subscribe for more tech & culture. The commercial production of this technology will also cripple the illegal trade in human organs fueled by lack of viable organ tissue. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Each component, needless to say, comes with its own unique ip perspectives and challenges. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Emerging 3d printed organs projects. 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials, design and modeling software, as well as services and/or processes to manufacture functional materials. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways.
3D printed organs from regenerative living cells . The biggest challenge of 3d printing organs:
3D 'bioprinters' could soon make organs and human tissue .... Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. The commercial production of this technology will also cripple the illegal trade in human organs fueled by lack of viable organ tissue. Emerging 3d printed organs projects. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and the researchers were actually able to manufacture a small heart with chambers, blood vessels, and human cells! Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. Each component, needless to say, comes with its own unique ip perspectives and challenges. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials, design and modeling software, as well as services and/or processes to manufacture functional materials. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. The biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: Professor tal dvir points out:
The Next Frontier for 3-D Printing: Human Organs . Scientists Are Using Special 3D Printers To Create Living Body Parts And Claim The Groundbreaking Method Will Soon Allow Them To Implant Printed Organs As Well.
Bioethics Obervatory - Institute of Life Sciences - UCV 3D .... The biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: Professor tal dvir points out: 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials, design and modeling software, as well as services and/or processes to manufacture functional materials. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. The commercial production of this technology will also cripple the illegal trade in human organs fueled by lack of viable organ tissue. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and the researchers were actually able to manufacture a small heart with chambers, blood vessels, and human cells! In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Each component, needless to say, comes with its own unique ip perspectives and challenges. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. Emerging 3d printed organs projects. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs.
3d printing organs - YouTube - One Day This Will Be Possible, And With A Desperate Global Shortage Of Organs For Transplant, The Medical Like Other Forms Of 3D Printing, Living Tissue Is Printed Layer By Layer.
5 Most Promising 3D Printed Organs for Transplant | All3DP. The commercial production of this technology will also cripple the illegal trade in human organs fueled by lack of viable organ tissue. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Each component, needless to say, comes with its own unique ip perspectives and challenges. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. The biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: Professor tal dvir points out: ► subscribe for more tech & culture. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and the researchers were actually able to manufacture a small heart with chambers, blood vessels, and human cells! In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Emerging 3d printed organs projects. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials, design and modeling software, as well as services and/or processes to manufacture functional materials. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology.
See-Through Body Organs May Help Scientists Create 3D ... . The Quest To 'Print Living Replacement Organs' Is Founded On Insatiable Need.
With Bioprinting the Impossible Seems Possible .... Emerging 3d printed organs projects. The biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. Professor tal dvir points out: The commercial production of this technology will also cripple the illegal trade in human organs fueled by lack of viable organ tissue. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Each component, needless to say, comes with its own unique ip perspectives and challenges. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials, design and modeling software, as well as services and/or processes to manufacture functional materials. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and the researchers were actually able to manufacture a small heart with chambers, blood vessels, and human cells!
Researcher Believes 3D Printing May Lead to the Creation ... , Imagine Printing A Human Liver.
3D Printing May Create Enhanced New Organs, Capable of .... Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. The commercial production of this technology will also cripple the illegal trade in human organs fueled by lack of viable organ tissue. The biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Emerging 3d printed organs projects. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials, design and modeling software, as well as services and/or processes to manufacture functional materials. Professor tal dvir points out: The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. Each component, needless to say, comes with its own unique ip perspectives and challenges. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and the researchers were actually able to manufacture a small heart with chambers, blood vessels, and human cells!
An Introduction to 3D Printed Organs and 3D Bioprinting ... , In The Case Of Organ Printing, The Material Being Used By The Printer Is A Biocompatible Plastic.
Infinite 3D-Printed Hearts in 'Pure Genius' Make Up For .... Emerging 3d printed organs projects. The commercial production of this technology will also cripple the illegal trade in human organs fueled by lack of viable organ tissue. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. The biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and the researchers were actually able to manufacture a small heart with chambers, blood vessels, and human cells! The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials, design and modeling software, as well as services and/or processes to manufacture functional materials. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. Professor tal dvir points out: Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. ► subscribe for more tech & culture. Each component, needless to say, comes with its own unique ip perspectives and challenges. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic.
3D Printers Could be Banned by 2016 for Bioprinting Human ... - Similar To Normal 3D Printers It Deposits Cells And Structural And Nutritional Material In The Attempt To Combine Different Tissues To Form Organs.
The First 3D Bioprinter That Can Print Body Parts for .... Emerging 3d printed organs projects. The biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: Professor tal dvir points out: In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials, design and modeling software, as well as services and/or processes to manufacture functional materials. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. The commercial production of this technology will also cripple the illegal trade in human organs fueled by lack of viable organ tissue. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and the researchers were actually able to manufacture a small heart with chambers, blood vessels, and human cells! The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. Each component, needless to say, comes with its own unique ip perspectives and challenges. ► subscribe for more tech & culture.
The Next Frontier for 3-D Printing: Human Organs : But While The Technology's Possibilities Are Exciting, Already There How Would You Bioprint A Heart?
Researcher Believes 3D Printing May Lead to the Creation .... 3d printing of human organs comprises the printing equipment, printing materials, design and modeling software, as well as services and/or processes to manufacture functional materials. Each component, needless to say, comes with its own unique ip perspectives and challenges. The biggest challenge of 3d printing organs: What keeps the organs working are blood vessels and the researchers were actually able to manufacture a small heart with chambers, blood vessels, and human cells! The commercial production of this technology will also cripple the illegal trade in human organs fueled by lack of viable organ tissue. The idea of bioprinting human organs is no longer some far off science fiction idea. In the case of organ printing, the material being used by the printer is a biocompatible plastic. Organ printing utilizes techniques similar to conventional 3d printing where a computer model is fed into a printer that lays down successive layers of plastics or wax until a 3d object is produced. Just like with an fdm or even sla printer, you use different printing materials to tackle different jobs. No one has printed fully functional, transplantable human organs just yet, but scientists are getting closer, making pieces of tissue that can be used to test drugs and designing methods to overcome the challenges of recreating the body's complex biology. Bioengineers at rice university created entangled cardiovascular networks similar to the body's natural passageways. Researchers from private companies and leading universities at the moment, it is like printing with only a few filaments. Emerging 3d printed organs projects. Professor tal dvir points out: ► subscribe for more tech & culture.
